Post-Test
Let's see what you learned...........
This post-test is only to gauge your ultrasound knowledge after completing your rotation.
No books or other study aids, please.
Multiple choice questions are self-explanatory. Choose the best response.
Some questions have corresponding pictures and/or U/S video clips. Click on the image/picture to make it larger. The video clips are in Vimeo format, and may be enlarged by clicking on the full-screen button in the lower left hand corner of the video.
Click on the “Post-test answer sheet” link below and print out the answer sheet. You will need to use this to document your answers to the questions on the test. Enter the password below for the post-test answer key. If you need the password, go to the Contact page and email me your request.
Good luck.
1. All of the following are true about ultrasound waves EXCEPT:
- Velocity of propagation is better in water than in air
- Higher frequency increases velocity
- The equation is: Velocity= Frequency X Wavelength
- Frequency is the number of cycles per second
- All of the above are correct
2. Which of the following is/are true?
- Ultrasound images (what you see) are based on the depth and direction of the returning echoes
- Depth is determined by the time elapsed between the signal and the received echo
- The returning intensity is proportional to the grayscale assignment on the screen (increased intensity=white, decreased=black)
- A and B
- All of the above
3. True / False: The amount of reflection is proportional to the difference in the acoustic impedance between the two media.
4. Attenuation is:
- The loss of signal energy as it passes through tissue
- The resistance to the propagation of sound
- The ability of the sound waves to discriminate between two different objects
- Anechoic signal caused by failure of the ultrasound beam to pass through an object
- None of the above
5. Which of the following is true about ultrasound and “gain”:
- The gain amplifies the returning echoes from all parts of the screen
- Returning echoes, by nature, are weaker than ultrasound pulses
- Distant structures tend to appear less echogenic
- A and B
- All of the above
6. What ultrasound setting allows you to adjust gain at a particular level/depth?
7. Identify the specific artifacts from the accompanying video and still images below:
7a.
- 7b.
- 7c.
- 7d.
8. In a FAST exam, the absence of “mirror artifact” in the right or left upper quadrant might be helpful in identifying what pathology (be specific)?
9. M-mode:
- Represents time on the horizontal axis
- Produces red color with flow towards the probe, and blue color with flow away from the probe
- Depicts the motion or deflection of the tissue relative to the transducer
- A and C
- All of the above
10. True / False: The FAST exam readily identifies around 50 mL of intraperitoneal blood.
11. Free fluid in trauma:
- Is initially anechoic
- Appears “pointy”
- Appears “rounded”
- Is difficult to distinguish from ascites
- A, B, and D
- All of the above
12. The FAST exam:
- Is more sensitive in obese patients
- Is used to identify free intraperitoneal or pericardial fluid in the setting of trauma
- Is sensitive for intra-abdominal organ injury
- Free fluid is most commonly found in the left upper quadrant
- A and B
- All of the above
13. Identify the structures on the cardiac view below:
Identify (A): __
Identify (B): __
Identify (C): __
Identify (B): __
Identify (C): __
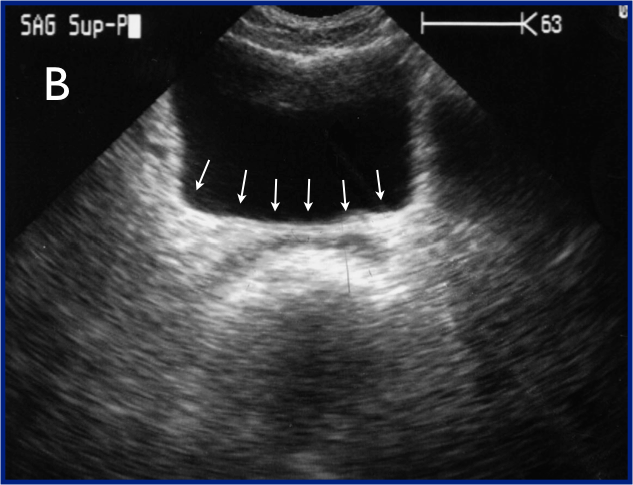
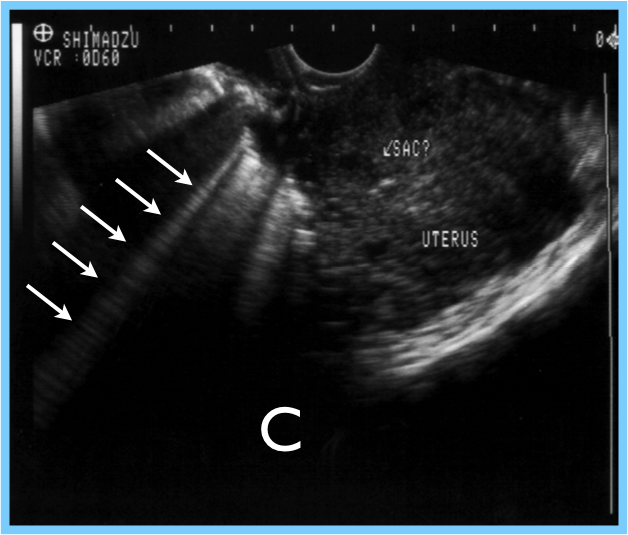
14. Name the four windows to evaluate for “free fluid”, circling the most sensitive of these locations for the identification of free fluid in a FAST exam:
15. True / False: The Suprapubic view is obtained just below (caudal) the level of the prostate in men, and the vaginal stripe in women.
16. In the RUQ (Perihepatic) view:
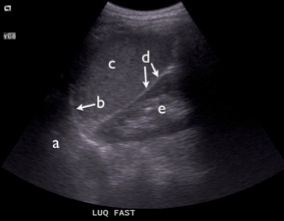
17. Identify the structures/areas on the LUQ view and state what is missing (inadequate) on this image below:
- __
- __
- __
- __
15. True / False: The Suprapubic view is obtained just below (caudal) the level of the prostate in men, and the vaginal stripe in women.
16. In the RUQ (Perihepatic) view:
- Perinephric fat is typically hyperechoic, and does not shift with movement
- Duodenal fluid, the gallbladder, and the IVC are all mimics for free fluid
- Perinephric fat tends to be even thickness
- Pleural fluid may present as an anechoic stripe above the diaphragm
- All of the above
17. Identify the structures/areas on the LUQ view and state what is missing (inadequate) on this image below:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
Missing: ____
b)
c)
d)
e)
Missing: ____
18. In the LUQ view:
19. In the Pelvic (Suprapubic) view:
20. In the subxiphoid (subcostal) cardiac view:
21. Pneumothorax is “ruled-out” (in the location under the probe) by either of the following two ultrasound findings:
1)
2)
22. In the Pneumothorax study with ultrasound:
23. Are the following pneumothorax videos positive (pneumothorax present) or negative (pneumothorax absent)? Please watch each video in its entirety.
- The phrenicocolic ligament restricts the flow of free fluid to the LUQ
- Blood preferentially flows between the left paracolic gutter to the LUQ
- The LUQ view is typically found more anterior and inferior as compared to the RUQ view
- The LUQ is the most easily visualized of the FAST views
- All of the above
19. In the Pelvic (Suprapubic) view:
- Seminal vesicles may be incorrectly identified as free fluid
- Gain artifact is a major issue in this view
- The probe should be angled to just below (caudal to) the prostate or vaginal stripe
- The probe should be placed in a periumbilical location
- A and B
- All of the above
20. In the subxiphoid (subcostal) cardiac view:
- RV or RA collapse may occur in an otherwise normal patient
- A little pericardial fluid may be completely normal
- Scans may be enhanced by obesity and pneumoperitoneum
- Imaging typically worsens when the patient takes a deep breath
- None of the above
21. Pneumothorax is “ruled-out” (in the location under the probe) by either of the following two ultrasound findings:
1)
2)
22. In the Pneumothorax study with ultrasound:
- Between two rib shadows, there is a notable echogenic line composed of the visceral and parietal pleura
- The transducer is placed longitudinally (pointed cranially) in the midclavicular line
- The transducer is moved inferiorly in a systematic fashion
- A and C
- All of the above
- None of the above
23. Are the following pneumothorax videos positive (pneumothorax present) or negative (pneumothorax absent)? Please watch each video in its entirety.
23A.
Positive or Negative
Positive or Negative
23B.
Positive or Negative
Positive or Negative
23C.
Positive or Negative
Positive or Negative
24. Which of the following can’t typically be ruled out by a FAST exam:
25. With regard to ectopic pregnancy:
26. Simple ovarian cysts are:
27. Arrange the following sonographic findings based on the order in which they appear during pregnancy, ordering first (1) to last (5):
28. What is the primary objective in 1st Trimester OB scans? ________________
29. True / False: Crown-rump length measurements exclude the yolk sac.
30. Bleeding between the endometrium and chorionic membrane is called ____________________.
31. True / False: A full bladder is necessary for an adequate transvaginal ultrasound.
32. ___________ are found just lateral and posterior to the body of the uterus.
33. Identify the structures on the still image from a transvaginal ultrasound:
- Viscus perforation
- Bowel wall contusion
- Pancreatic trauma
- Renal pedicle injuries
- Retroperitoneal hemorrhage
- All of the above
25. With regard to ectopic pregnancy:
- Typically occur in the ovaries
- The B-hCG always rises less than 50% every 2 days
- If a patient has a B-hCG of <500, then an ultrasound is not helpful to evaluate for ectopic
- The incidence of heterotopic pregnancy is around 1 in 400
- None of the above
26. Simple ovarian cysts are:
- Thin-walled
- Anechoic
- Spherical
- No loculations
- All of the above
27. Arrange the following sonographic findings based on the order in which they appear during pregnancy, ordering first (1) to last (5):
- Fetal pole
- Double decidual sign
- Fetal heart tones
- Yolk sac
- Thickened endometrium
28. What is the primary objective in 1st Trimester OB scans? ________________
29. True / False: Crown-rump length measurements exclude the yolk sac.
30. Bleeding between the endometrium and chorionic membrane is called ____________________.
31. True / False: A full bladder is necessary for an adequate transvaginal ultrasound.
32. ___________ are found just lateral and posterior to the body of the uterus.
33. Identify the structures on the still image from a transvaginal ultrasound:
a) __ (the entire organ)
b) __ (the general area)
c) __
d) __
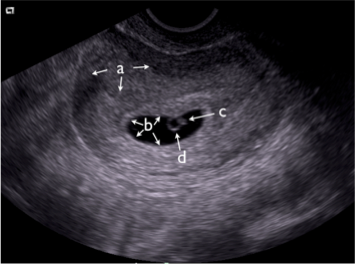
34. Identify the pathology in the
transvaginal OB scan to the right:
transvaginal OB scan to the right:
35. Identify the pathology in the transvaginal OB scan to the right:
36. ________ may cause shadowing in the uterus due to internal fibrotic changes and calcifications (see the corresponding OB video to the right)
37. Identify the following structures on transverse view of the upper midline abdomen. First, watch the corresponding video to the right. Then, identify the labeled structures on the image below.
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
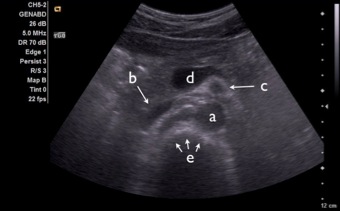
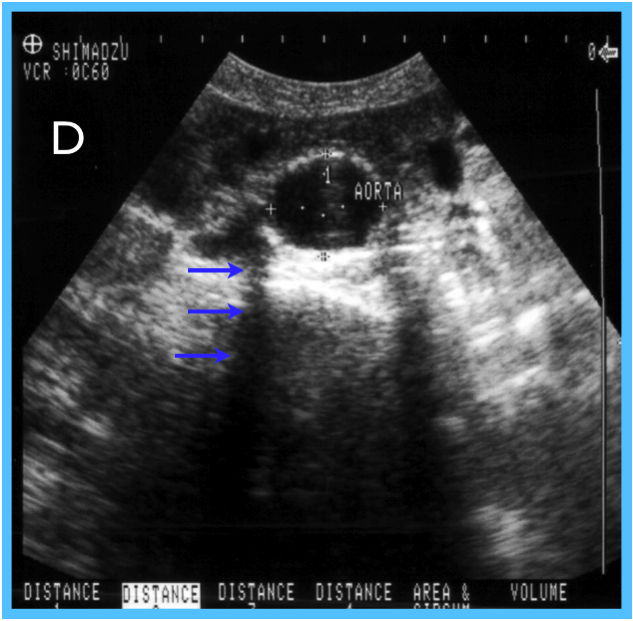
38. The aorta:
39. AAAs:
40. Ultrasonography for AAA:
41. True / False: The aorta diameter should be measured in transverse from inside wall to inside wall.
42. In soft tissue ultrasound:
43. Name 2 sonographic findings in abscesses:
1)
2)
- Is approximately 2cm as it enters the abdomen and then gradually increases in size distally
- Gives off, in the following order, the celiac trunk, the superior mesenteric artery, the inferior gastric artery, the inferior mesenteric artery, and the renal arteries
- Bifurcates into the common iliac arteries at approximately the level of the umbilicus (L4 level)
- B and C
- All of the above
39. AAAs:
- Are defined as an abnormal focal dilation of the vessel wall that measures greater than 5cm
- Expand at an average rate of 2-3 cm per year
- When ruptured, tend to do so intraperitoneally
- An intervention is often recommended if the aneurysm grows more than 1 cm per year or it is bigger than 5.5 cm
- None of the above
40. Ultrasonography for AAA:
- Has been reported to be nearly 100% sensitive for detecting AAA, assuming the study is adequate
- Has a high sensitivity for detecting extraluminal blood from a ruptured AAA
- Usually incorporates a 2.5-5 MHz curved array probe
- A and C
- All of the above
41. True / False: The aorta diameter should be measured in transverse from inside wall to inside wall.
42. In soft tissue ultrasound:
- Fascial planes are hyperechoic
- Muscle has a characteristic striated appearance
- Lymph nodes have echogenic centers with hypoechoic rims
- A and B
- All of the above
43. Name 2 sonographic findings in abscesses:
1)
2)
44. Name the sonographic finding in the soft tissue scan to the right.
45. What sonographic "sign" demonstrated in the soft tissue scan to the right confirms the presence of an abscess?
46. What is the finding/structure in this soft tissue ultrasound of the upper thigh and inguinal region.
47. Diagnosis in this buttock ultrasound.
48. With ultrasound-guided vascular access:
49. Sonographically, arteries tend to be:
50. True / False: Low frequency, high penetration is ideal for vascular access.
51. True / False: In ultrasound-guided venous access, a flash of blood is adequate to confirm that the catheter can be advanced into the lumen.
- The transverse approach is typically easier to learn
- A disadvantage of the longitudinal approach is that you must scan back and forth to locate the needle tip as you advance
- The one person technique is preferable in a busy ED
- A and C
- All of the above
49. Sonographically, arteries tend to be:
- Pulsatile
- Collapsible
- Thin-walled
- All of the above
- None of the above
50. True / False: Low frequency, high penetration is ideal for vascular access.
51. True / False: In ultrasound-guided venous access, a flash of blood is adequate to confirm that the catheter can be advanced into the lumen.
52. Answer the following from the video to the right:
- Location of the DVT study (Common femoral vein or Popliteal vein)
- Is a thrombus present: Yes or No
53. Answer the following from the video to the right:
- Location of the DVT study (Common femoral vein or Popliteal vein)
- Is a thrombus present: Yes or No
54. Diagnosis in this patient with a red, painful calf (see corresponding video to the right):
55. What is the definition of a DVT by ultrasound (with regard to compressibility)?
__________________________________
56. In emergency venous compression ultrasonography:
57. Name 3 ways to position the patient for the popliteal evaluation:
1)
2)
3)
58. True / False: The popliteal vein is deep to the popliteal artery.
59. Name 4 sonographic findings in acute cholecystitis:
1)
2)
3)
4)
60. What is the rule for common bile duct size based on age? __________
__________________________________
56. In emergency venous compression ultrasonography:
- The linear probe is typically used
- The patient is maintained (if possible) in Trendelenburg
- Augmentation, spontaneity, and respiratory variation are documented for an Emergency Ultrasound DVT exam
- A and B
- None of the above
57. Name 3 ways to position the patient for the popliteal evaluation:
1)
2)
3)
58. True / False: The popliteal vein is deep to the popliteal artery.
59. Name 4 sonographic findings in acute cholecystitis:
1)
2)
3)
4)
60. What is the rule for common bile duct size based on age? __________
61. Identify the three structures in the Portal triad from the image to the right:
A)
B)
C)
A)
B)
C)
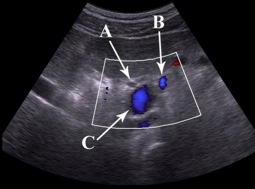
62. With regard to RUQ ultrasound:
63. Describe the criteria for a true sonographic Murphy’s sign: _____________
64. True / False: Sludge has a low-level echogenicity (less echoic than stones) and fails to cause acoustic shadowing.
- A contracted gallbladder is common in acute cholecystitis
- Normal gallbladder wall thickness is < 7mm
- The most common cause of gallbladder wall thickening is acute cholecystitis
- Ultrasound has a high sensitivity for detecting common bile duct stones
- None of the above
63. Describe the criteria for a true sonographic Murphy’s sign: _____________
64. True / False: Sludge has a low-level echogenicity (less echoic than stones) and fails to cause acoustic shadowing.
65. Describe the two pathologic findings on the ultrasound to the right:
1)
2)
1)
2)
66. What is the diagnosis in this patient with RUQ pain and the following ultrasound to the right?
67. Choose the primary indication(s) for emergency renal ultrasound:
68. In renal ultrasound, the following is/are correct:
69. With regard to hydronephrosis:
- Rule out renal tumors
- Evaluate for painless hematuria
- Search for an etiology of acute renal failure
- Evaluate patients with a clinical suspicion of ureteral colic
- Look for urinary retention
- C, D and E
- All of the above
68. In renal ultrasound, the following is/are correct:
- Your views may be improved by angling the probe indicator posteriorly in the orientation of the ribs
- Perinephric fat is commonly seen between the kidney and the adjacent liver or spleen
- The normal ureter is not visualized
- Bladder volume may be estimated by taking 3 dimensions (in centimeters), and multiplying them together (X times Y times Z) for a volume in milliliters
- The left kidney is often more difficult to visualize due to a smaller sonographic window
- A and D
- All of the above
69. With regard to hydronephrosis:
- Calyceal dilation is reflected as hyperechoic areas in the renal sinus
- Ureteral stones are commonly visualized in the mid-ureter
- Color flow may be placed over the kidney to differentiate vascular structures versus hydronephrosis
- B and C
- None of the above
70. Watch the ultrasound clip of the kidney and classify the renal cyst as either simple or complex (circle your answer):
71. Indicate the degree of hydronephrosis in the following video (MILD, MODERATE, or SEVERE):
72. What is the sonographic finding and its clinical significance, as seen in the video to the right?
73. Name the 4 basic views for a limited echo exam:
1)
2)
3)
4)
1)
2)
3)
4)
74. Name the cardiac view and the labeled structures in the video to the right:
View: ____
A)
B)
C)
D)
View: ____
A)
B)
C)
D)
75. Name the cardiac view and the labeled chambers in the video to the right:
View: ____
A)
B)
C)
D)
View: ____
A)
B)
C)
D)
76. What is the normal RV/LV size ratio: ______________
77. True / False: The IVC is dilated in tamponade.
78. Name the 2 specific echocardiographic findings (from the video to the right) in this patient with pleuritic chest pain:
1)
2)
1)
2)
79.*Are the following patients hypovolemic, euvolemic, or hypervolemic? (circle one)
PATIENT #1
PATIENT #2
80. Estimate the ejection fraction (EF%) in the video to the right:
- 0-30
- 30-50
- 50-70
- >70
81. Estimate the ejection fraction (EF%) in the video to the right:
- 0-30
- 30-50
- 50-70
- >70
82. What positioning maneuver can be used when a supine patient has poor cardiac windows?
83. From the video to the right, identify the cardiac view, the diagnosis (pathology), and 2 ultrasonographic findings that support your diagnosis:
View: __________________
Diagnosis: _______________
1)
2)
View: __________________
Diagnosis: _______________
1)
2)
84. Fill in the blank with the following ultrasound terms: Depth, Focus, Gain, Zoom and Frequency. (use each term only once)
85. True / False: Anisotropic tissue varies in appearance from bright to black based on the scanning angle (angle of insonation).
- ________ narrows the US beam at the depth of interest.
- ________ adjusts the number of centimeters to the bottom of the screen.
- ________ expands the area of interest on the viewing screan.
- ________ improves resolution.
- ________ augments the ultrasound signal on the viewing screen.
85. True / False: Anisotropic tissue varies in appearance from bright to black based on the scanning angle (angle of insonation).
Congratulations!! You're done!!