Pre-Test 2
This pre-test is only to gauge your ultrasound knowledge prior to the U/S rotation.
No books or other study aids, please.
Multiple choice questions are self-explanatory. Choose the best response.
Some questions have corresponding pictures and/or U/S video clips (designated by a “*”). For the videos, click on the link that follows, which directs you to a separate web page. This page houses ALL of the videos, in order, corresponding to the questions.
Click on the “Pre-test answer sheet” link below and print out the answer sheet. You will need to use this to document your answers to the questions on the test. Enter the password below for the pre-test answer key. If you need the password, go to the Contact page and email me your request.
Good luck.
No books or other study aids, please.
Multiple choice questions are self-explanatory. Choose the best response.
Some questions have corresponding pictures and/or U/S video clips (designated by a “*”). For the videos, click on the link that follows, which directs you to a separate web page. This page houses ALL of the videos, in order, corresponding to the questions.
Click on the “Pre-test answer sheet” link below and print out the answer sheet. You will need to use this to document your answers to the questions on the test. Enter the password below for the pre-test answer key. If you need the password, go to the Contact page and email me your request.
Good luck.
1. Which of the following is/are true?
- Ultrasound images (what you see) are based on the depth and direction of the returning echoes
- Depth is determined by the time elapsed between the signal and the received echo
- The returning intensity is proportional to the grayscale assignment on the screen (increased intensity=white, decreased=black)
- A and B
- All of the above
2. Attenuation is:
- The loss of signal energy as it passes through tissue
- The resistance to the propagation of sound
- The ability of the sound waves to discriminate between two different objects
- Anechoic signal caused by failure of the ultrasound beam to pass through an object
- None of the above
3. Free fluid in trauma:
4. Identify the structures on the cardiac view below:
- Is initially anechoic
- Appears “pointy”
- Appears “rounded”
- Is difficult to distinguish from ascites
- A, B, and D
- All of the above
4. Identify the structures on the cardiac view below:
Identify (A): __
Identify (B): __
Identify (C): __
Identify (B): __
Identify (C): __
5. In the pericardial view:
- RV or RA collapse may occur in an otherwise normal patient
- A little pericardial fluid may be completely normal
- Scans may be enhanced by obesity and pneumoperitoneum
- Imaging typically worsens when the patient takes a deep breath
- None of the above
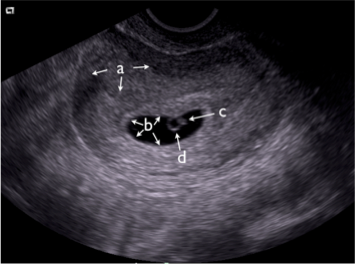
6. Identify the structures on the still image from a transvaginal ultrasound:
a) __ (the entire organ)
b) __ (the general area)
c) __
d) __
b) __ (the general area)
c) __
d) __
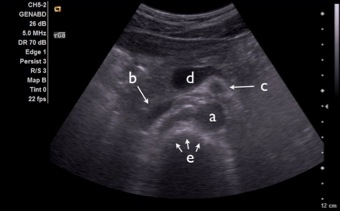
7. Identify the following structures on transverse view of the upper midline abdomen. First, watch the corresponding video to the right. Then, identify the labeled structures on the image below.
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
8. What sonographic "sign" demonstrated in the soft tissue scan to the right confirms the presence of an abscess?
9. With ultrasound-guided vascular access:
- The transverse approach is typically easier to learn
- A disadvantage of the longitudinal approach is that you must scan back and forth to locate the needle tip as you advance
- The one person technique is preferable in a busy ED
- A and C
- All of the above
10. In emergency venous compression ultrasonography:
- The linear probe is typically used
- The patient is maintained (if possible) in Trendelenburg
- Augmentation, spontaneity, and respiratory variation are documented for a full exam
- Evaluation for noncompressibility of the common femoral vein and the popliteal vein is adequate
- A and D
- None of the above
11. With regard to RUQ ultrasound:
- A contracted gallbladder is common in acute cholecystitis
- Normal gallbladder wall thickness is < 7mm
- The most common cause of gallbladder wall thickening is acute cholecystitis
- Ultrasound has a high sensitivity for detecting common bile duct stones
- None of the above
12. In renal ultrasound, the following is/are correct:
- Your views may be improved by angling the probe indicator posteriorly in the orientation of the ribs
- Perinephric fat is commonly seen between the kidney and the adjacent liver or spleen
- The normal ureter is not visualized
- Bladder volume may be estimated by taking 3 dimensions (in centimeters), and multiplying them together (X times Y times Z) for a volume in milliliters
- The left kidney is often more difficult to visualize due to a smaller sonographic window
- A and D
- All of the above
13. Name the cardiac view and the labeled chambers in the video to the right:
View: ____
A)
B)
C)
D)
View: ____
A)
B)
C)
D)
14. Estimate the ejection fraction (EF%) in the video to the right:
- 0-30
- 30-50
- 50-70
- >70
Congratulations!! You're done!!